Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, followed by specific tests to confirm the presence and extent of a blood clot.
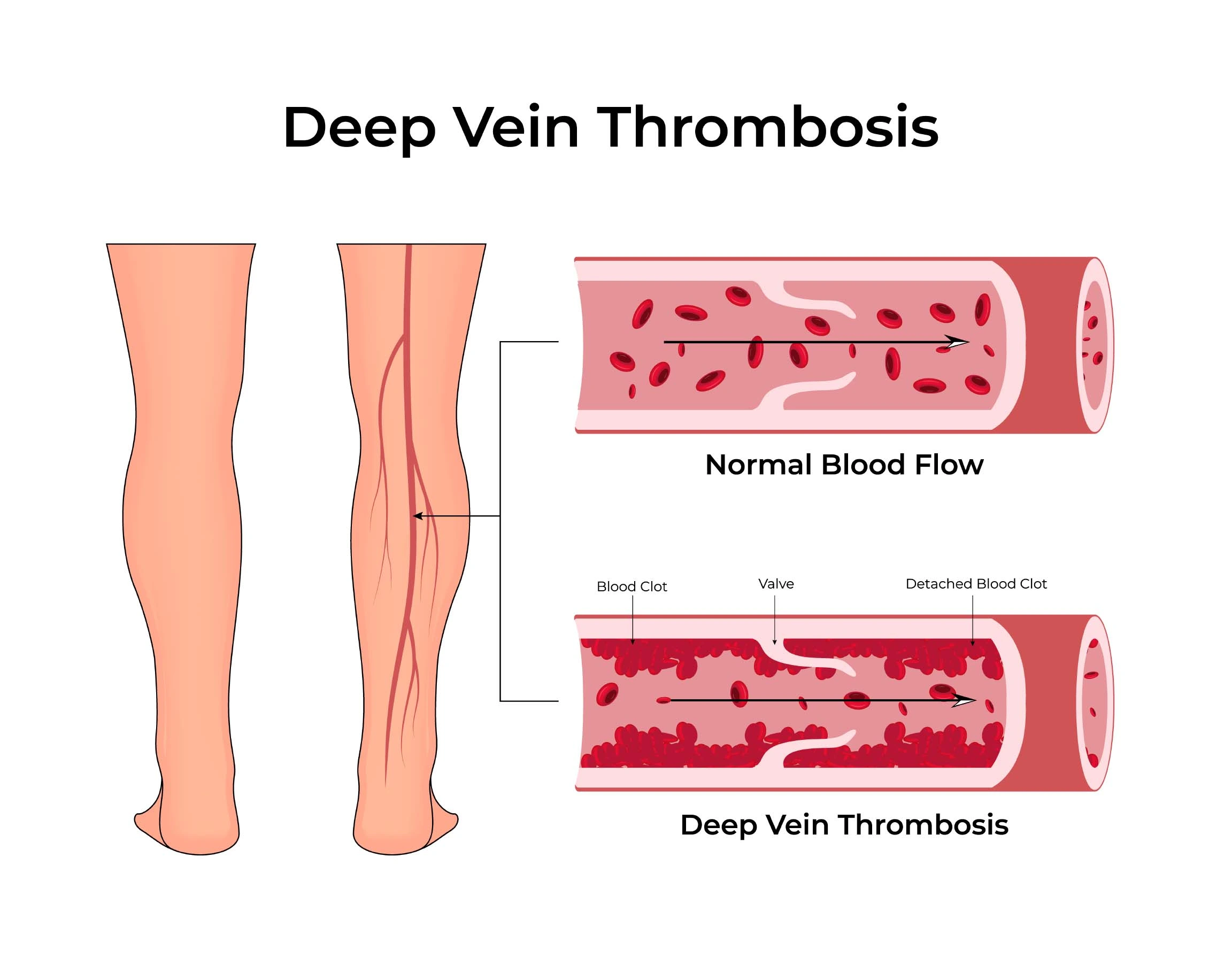
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious vascular condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs, obstructing normal blood flow. Common deep vein thrombosis causes include prolonged immobility, surgery, injury, or genetic clotting disorders. Typical deep vein thrombosis symptoms are leg swelling, pain, warmth, and redness. Without prompt care, deep vein thrombosis complications such as pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening.
Effective deep vein thrombosis treatment may involve anticoagulant medication, compression therapy, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Preventive strategies focus on regular movement, hydration, and maintaining a healthy weight — key aspects of deep vein thrombosis prevention and management. For mild discomfort, home remedies for deep vein thrombosis like leg elevation and gentle exercise can aid recovery under medical supervision.
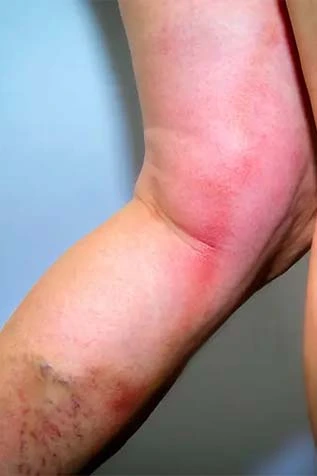
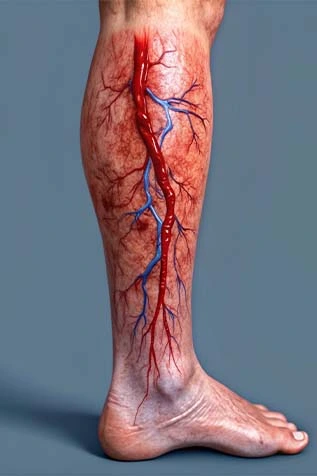
Long flights, hospitalization, or paralysis can reduce blood flow and increase clot risk
Orthopedic and pelvic operations temporarily slow circulation, making clots more likely.
Hormone therapy or birth control pills can elevate clotting tendencies in some individuals.
The pregnancy and postpartum phases naturally increase vein pressure and clot risk.
Obesity and smoking impair circulation and contribute to venous blockages.
A prior Deep vein thrombosis or family history of venous thromboembolism raises recurrence risk significantly.
Involves the veins above the knee. This type is more serious because clots here are more likely to break off and cause pulmonary embolism.
Occurs in the veins below the knee—like the posterior tibial, peroneal, or muscular veins of the calf.
Affects the deep veins of the arm, such as the subclavian or axillary veins. It can occur due to catheters, pacemaker leads.
Develops due to identifiable causes like surgery, trauma, pregnancy, or prolonged immobility.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, followed by specific tests to confirm the presence and extent of a blood clot.

A non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to visualize blood flow and detect clots in the deep veins.
a specialized blood test designed to assess an individual’s risk of developing abnormal blood clots. It evaluates various genetic and acquired factors in the blood that may contribute to clotting disorders.
Medications such as heparin, warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants prevent clot enlargement and recurrence.
Clot-dissolving drugs used in severe or high-risk cases to restore blood flow.
Getting up and moving regularly, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding sitting or lying still for long periods.
Inserted into the main vein to trap clots and prevent them from reaching the lungs when anticoagulants aren’t suitable
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a preventable and manageable condition when detected early. Understanding deep vein thrombosis causes, recognizing symptoms, and starting prompt deep vein thrombosis treatment with anticoagulants are vital to avoid serious complications. Consistent movement, hydration, and healthy lifestyle choices aid deep vein thrombosis prevention. With proper management and guided home remedies for deep vein thrombosis, long-term vascular health and recovery can be effectively maintained.
Got a question?

Yes, in many cases Deep Vein Thrombosis is silent until a complication like pulmonary embolism occurs.
With proper treatment, most cases resolve completely. Long-term management focuses on preventing recurrence.
Gentle movement and walking improve blood flow, but strenuous exercise during acute DVT should be avoided until cleared by a doctor.
It’s a chronic complication after Deep Vein Thrombosis characterized by pain, swelling, heaviness and skin changes due to vein damage.
If left untreated, deep vein thrombosis can lead to life-threatening pulmonary embolism, chronic leg swelling, and long-term vein damage.