- Avis Hospitals
- No Comments
Varicose veins or twisted bulged veins are common in older people and the female population though they may be common among people of all ages. This condition occurs due to venous insufficiency or the inability of veins to pump blood. Varicose veins cause pain, heaviness and inflammation. So, do varicose veins affect the older population only? And at what age do varicose veins show up?
Age is one of the common factors affecting varicose veins since older age can cause a reduction in vein health and elasticity and vein valve functioning. However, with factors such as genetics and lifestyle choices at play, the age at which varicose veins show up may be considerably lesser.
So, when do these varicose veins show up? Do they appear only in older age or can they appear at any age in life? This article explores the effects of age on the development and progression of varicose veins, factors responsible for early development and how early intervention can prevent further worsening of the condition.
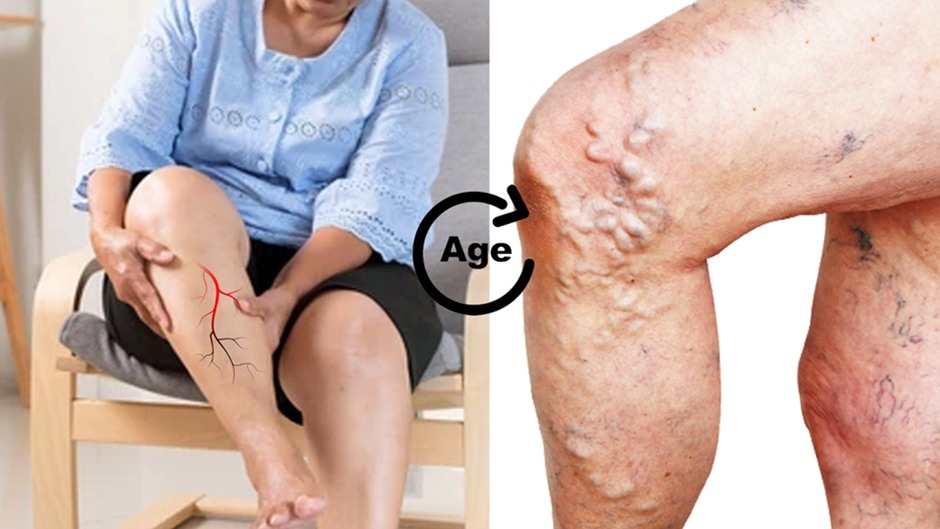
Varicose veins or twisted bulged veins are common in older people and the female population though they may be common among people of all ages. This condition occurs due to venous insufficiency or the inability of veins to pump blood. Varicose veins cause pain, heaviness and inflammation. So, do varicose veins affect the older population only? And at what age do varicose veins show up?
Age is one of the common factors affecting varicose veins since older age can cause a reduction in vein health and elasticity and vein valve functioning. However, with factors such as genetics and lifestyle choices at play, the age at which varicose veins show up may be considerably lesser.
So, when do these varicose veins show up? Do they appear only in older age or can they appear at any age in life? This article explores the effects of age on the development and progression of varicose veins, factors responsible for early development and how early intervention can prevent further worsening of the condition.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are palpable swollen veins or twisted veins that appear on the lower extremities of the body such as legs, feet and ankles. The vein valves or walls may sometimes malfunction owing to advancing age, hormone fluctuations, genetics, obesity and sedentary lifestyle.
Veins are a part of the body’s blood circulation system and transport blood from different parts of the body to the heart for oxygenation. Veins in the lower parts of the body such as legs have to work harder against gravity to push blood to the heart.
A dysfunctioning vein wall or valve can cause the blood to accumulate in the vein instead of regulating the flow to the heart. The accumulated blood causes the vein to swell and inflame resulting in varicose veins.
The tissues surrounding the varicose vein may start experiencing irritation and inflammation resulting in skin changes. Fluid leak from the varicose vein into the surrounding tissue may cause further damage to the area. Further worsening of the condition may result in water retention.
Skin hardening and skin ulceration may also occur if the condition is not medically managed. Severe venous insufficiency can lead to deep vein thrombosis which can get fatal without immediate medical intervention.
Risk Factors For Varicose Veins
Several risk factors may result in the development of varicose veins such as:
Age
Advancing age can cause the veins to lose their elasticity and vein valves to lose their functioning resulting in varicose veins.
Genetics
Genetics plays a vital role in varicose veins with a family history of venous insufficiency increasing the chance of an individual inheriting weak vein wall or valves, thus developing varicose veins.
Genes play an important role in individuals experiencing an early onset of varicose veins, much before the average age at which varicose veins show up.
Hormone fluctuations
Elevated levels of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen can increase vein elasticity and weaken them increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Menstruation, pregnancy, menopause and the use of hormonal birth control may increase a woman’s chance of developing varicose veins.
Lifestyle factors
Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle increase the chance of developing varicose veins since such individuals often experience poor blood circulation. Prolonged standing and sitting due to job nature is also a risk factor for varicose veins.
At What Age Do Varicose Veins Show Up?
Varicose veins generally appear in the population over 40 years of age with women showing higher numbers than men.
However, it is not uncommon for young people over the age of 20 to develop varicose veins.
Since genetics is one of the important factors influencing venous insufficiency, young adults with a family history of venous insufficiency, reduced production of collagen and estrogen, genetic mutations and variations in genes such as the FOXC2 gene and the HSP90B1 gene.
Women, due to hormonal shifts can experience varicosity at an early age during stages such as menstruation, pregnancy and menopause. Hormonal birth control can also increase varicose vein risk making women in as early as their 20s develop venous insufficiency, especially when family history plays a role.
Varicose Veins in Teenagers
Venous insufficiency in teens is relatively uncommon but not unheard of.
Genetics is the most common reason behind varicose veins in this age group.
Having parents and grandparents with varicose veins can increase the chances of developing varicosity even among the younger population.
Among women, changes during the menstrual cycle can increase the chances of developing varicose veins, especially when genetics is at play.
Sedentary lifestyle is another common causative factor for varicose veins, especially among the younger generation.
Long hours spent on gadgets, playing computer games and watching TV reduces movement and exercise hampering blood circulation, especially in the legs.
List of the detailed causes of varicose veins in teenagers includes:
Genetics
Genetics is one of the main influencing factors for varicose veins in teenagers.
A teenager with a family history of venous insufficiency is more likely to develop varicose veins from a young age.
Inherited genes can influence
- Vein Wall Strength
Vein wall strength is passed down from one generation to another. Parents or grandparents having weak vein walls are likely to pass down the same character to their kids or grandkids.
Poor vein wall strength can make veins more prone to stretching and bulging, resulting in the early formation of varicose veins.
- Valve Functioning
Vein valves are responsible for ensuring the one-way movement of blood back to the heart. A faulty valve may fail to regulate blood circulation, resulting in blood pooling in the vein.
This results in the swelling and twisting of the vein, resulting in varicose veins.
- Collagen and Elastin
Collagen and elastin are two vital proteins that are essential for the strength and elasticity of veins. While collagen maintains the strength and elasticity of veins, elastin maintains the elasticity and allows veins to get back to their original form.
Since the production of collagen and elastin depends on genes, a family history of varicose veins can increase the chances of teenagers developing varicose veins.
Puberty
Kids experience puberty during their teens. This is a phase of hormonal fluctuations, especially for girls.
Hormones such as progesterone and estrogen can fluctuate during puberty, especially for females experiencing menstrual cycles and those on hormonal birth control.
Fluctuations in these hormones can impact vein health and elasticity and vein valve functioning leading to varicose veins.
Obesity
Lack of exercise, a sedentary lifestyle and poor eating habits can all contribute to obesity, a factor becoming common in teenagers who spend hours either in classes or in front of gadgets.
Excess body weight can stress the veins, impede blood circulation and increase the risk of varicose veins.
While many factors can lead to venous insufficiency and varicosity in teenagers, early intervention and management can help control the spread of varicose veins.
Prevention and Management of Varicose Veins in Teenagers
Among teenagers, varicose veins occurring due to genetics and hormonal fluctuations cannot be prevented. However, lifestyle modifications and home remedies can help resolve symptoms, if any, and prevent the spread of the condition.
Here are some steps to manage varicose veins in teenagers and individuals in their 20s.
Staying Active
Exercising and staying active help improve blood circulation and help with varicose veins. Walking, jogging, stretching, cycling and swimming are some of the exercises that can be included in the daily routine.
Individuals in sedentary jobs, or jobs involving prolonged standing or sitting, should take breaks for quick exercises and stretching.
Eating Healthy
Eating a balanced, nutritious diet with whole produce and grains and staying away from junk and processed foods and drinks are essential for preventing varicose veins and curbing their spread.
Home Remedies
Compression stockings and leg elevation are recommended to encourage blood flow and reduce pain and inflammation, if influenced by varicose veins and its symptoms.
Medical Intervention
Those experiencing pain, heaviness or inflammation in the legs should consult a varicose veins expert who will do a physical examination, run tests and suggest treatments or remedies as necessary.
Varicose veins in teenagers may be relatively uncommon, but not unheard of. Recognising the symptoms and getting timely medical evaluation and treatment are essential to maintain vein health and prevent complications.
Varicose Veins in Young Adults and Middle Age (20 – 40 years)
While it is a common perception that varicose veins are common among the older population, it is also seen in adults in their 20s and 30s.
Individuals with a genetic predisposition are at a higher risk in this age group. Additionally, women going through stages of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy and those on birth control are also susceptible to developing varicose veins.
Here are the common causes of varicose veins in young adults.
Genetics
As with any age group, genetics is the strongest risk factor for varicose veins for those in their 20s and 30s.
Having parents and grandparents with venous insufficiency can cause individuals to inherit poor vein wall strength, impaired vein functioning or lower production of collagen and elastin leading to varicose veins.
Hormones
Women are at a higher risk of developing varicose veins in this age group owing to the hormonal changes.
Many women utilising hormonal birth control experience fluctuations in hormones, resulting in varicose veins.
Pregnancy also causes many changes such as hormone fluctuations, increased blood volume and growth in the uterus size, all of which can contribute to varicose veins.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet choices, and lack of exercise are common risk factors for varicose veins across all age groups.
Trauma or injury to the legs, more specifically the veins, can damage the vein walls or valves, leading to varicose veins. Tight clothing and high heels are also known to contribute to varicose veins and must be avoided.
Common symptoms of varicose veins include visible, twisted and swollen veins under the skin that may cause pain, heaviness, discomfort and inflammation.
Itching, irritation and burning around the veins is common. Skin changes such as discolouration, thickening of the veins, and hardening of the skin surrounding the varicose veins can also occur.
Prevention and Management of Varicose Veins in 20s and 30s
Preventing and managing varicose veins in the 20s and 30s include lifestyle modifications and medical intervention when needed.
Strategies to prevent and manage varicose veins in the age group of 20 to 40 can include:
Lifestyle Modifications
Leading a healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing varicose veins and its spread. Exercising regularly (walking, jogging, swimming, cycling), eating a nutritious and balanced meal, staying hydrated and maintaining sleep hygiene are important.
Consuming junk, processed foods, foods and drinks high in salt and sugar, alcohol, and nicotine must be avoided.
Diet should consist of whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds and healthy fats.
Medical Intervention
Individuals suffering from varicose veins should get a medical evaluation at the earliest. Treatment options may include home remedies and minimally invasive procedures in early stages or more invasive surgeries in advanced cases.
Medical checkups and regular follow-up visits are essential to help prevent further spread of the condition while maintaining vein health and preventing complications.
Home Remedies
Leg elevation can help blood circulation and reduce pain, inflammation and swelling. Compression stockings are often recommended to reduce pain and improve blood circulation. Leading a healthy lifestyle and including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory foods in the diet are also important.
While the ages of 20s and 30s may be considered a bit early for developing varicose veins, cases do happen. Early medical intervention and lifestyle changes, especially in the initial stages, are essential to preserve vein health and prevent further complications that may occur with advancing age.
Varicose Veins in Adults Aged 40 and Above
Age can have a significant effect on varicose veins, with advancing age causing wear and tear on vein walls and valves.
People over the age of 40 are at a higher risk of developing varicose veins due to the combination of advanced age, changing hormones, lifestyle factors and underlying health conditions.
Some of the factors influencing varicose veins in adults 40 and above are:
Advancing Age
Advancing age can reduce vein wall health and vein valve health, leading to the formation of varicose veins.
Hormonal Variations
Women in this age group experience menopause, which can cause hormonal fluctuations leading to varicose veins. Some women may undergo hormone replacement therapy to counter the effects of menopause, which can again cause varicosity.
Lifestyle Factors
Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor food habits and jobs involving prolonged standing and sitting can all contribute to varicose veins in this age group.
Ageing people have reduced energy to stay active or exercise and may embrace a more slow-paced lifestyle which can contribute to the condition.
Health Conditions
People with underlying health conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, chronic venous insufficiency or deep vein thrombosis can be at a higher risk of developing varicosity due to the already existing circulation problems.
Common symptoms include pain, heaviness and discomfort in legs, skin changes, skin hardening, itching, burning, cramping and ulcers in the affected area.
Complications such as ulceration, bleeding, slow healing of wounds and blood clot formation due to untreated varicose veins are much higher in this age group. Timely diagnosis and treatment are vital.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are common across various age groups. However, the causative factors may vary slightly depending on age. Genetics and lifestyle factors are common contributors among all age groups.
Exercising, walking, jogging and cycling can improve the symptoms and prevent the varicose veins from spreading. Irrespective of age, maintaining healthy food habits, exercising and following the instructions of varicose veins specialists, such as the team of experts at Avis hospitals, will help people belonging to all age groups manage symptoms and prevent the condition from spreading or worsening.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
At what age is it normal to get varicose veins?
Varicose veins are considered most common in people over 50 years, where advancing age may reduce vein health and elasticity. However, teenagers and those in their 20s, 30s, and 40s may also develop varicose veins due to factors such as genetics and poor lifestyle habits.
What are the first signs of varicose veins?
Varicose veins can show up as twisted or bulged veins under the skin. For some people, this may end up being just a cosmetic concern with no other symptoms. However, others may experience symptoms such as pain, heaviness or inflammation in the legs or the area where the varicose veins develop. Skin changes such as rashes, reddening, and irritation may also occur.
Is it OK to have varicose veins?
Varicose veins are a common condition, and many adults are affected by it. For some, it can be only a cosmetic condition due to the appearance of twisted swollen veins under the skin. For others, the symptoms may be mild but can be managed with home remedies and minimal intervention procedures. However, severe cases of varicose veins with chronic severe pain and discomfort accompanied by skin hardening, oedema, or the appearance of slow-healing ulcers or bleeding ulcers may need immediate medical intervention.
Can varicose veins go away naturally?
Varicose veins are a long-term condition and cannot go away naturally on its own without any treatment. Medically treating varicose veins may involve procedures such as Radio Frequency Ablation, Endovenous Laser Ablation, sclerotherapy, cryosclerotherapy or vein stripping and ligation based on the stage and severity of the condition.
Can I live normally with varicose veins?
It is possible to live normally with varicose veins with timely identification of the condition and medical intervention. The doctor may do a physical examination and run medical tests to identify the severity. Based on this, they may suggest remedies and treatment protocols. It is important to follow these instructions and continue follow-up visits to live normally with varicose veins.
